I/O Hardware
Inside I/O Device
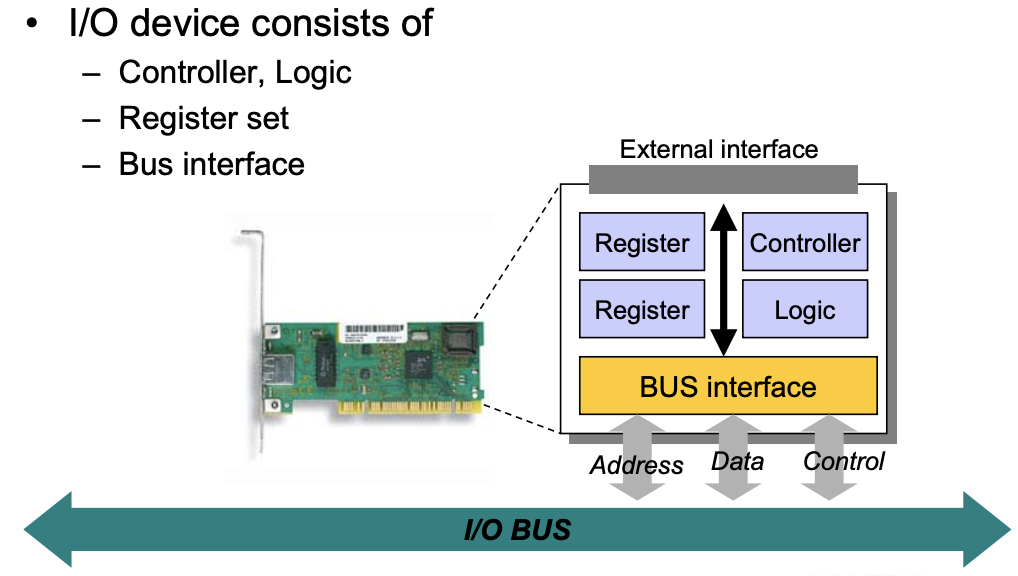
- Status Register : 장치의 상태를 보여주는 Register
- Control Register : 장치의 동작을 결정하는 Register
-
Data Register : 입출력할 데이터를 잠시 보관하는 Register
- I/O Device의 Register에 접근하는 두가지 방법 :
- Memory mapped I/O
- Port mapped I/O
- OS가 I/O Device를 제어한다는 것은 I/O Device에 있는 Register들을 Programming한다는 것임
I/O Devices의 분류
[1] Character Devices : Data transfer가 Character단위로 이뤄짐
- Mouse
- OS와 Mouse driver의 동작
- Background Application이 mouse 움직이나 클릭을 기다림
- mouse 움직이나 클릭이 packet형태로 Mouse driver에게 전달
- Mouse driver는 OS에게 Mouse event의 존재를 알리기 위해 event queue에 넣게됨
- OS는 시간이 날 때 마다 notify를 받아서 event queue에 접근해 event에 대한 handling을 하게됨
- Mouse Driver의 역할 요약
- Mouse Interrupt 발생 시, Mouse의 Data Register에서 값을 읽어오는 역할
- Interrupt를 Event로 바꾸어 주는 역할
- OS와 Mouse driver의 동작
- Terminal
- Keyboard Driver의 역할 요약
- Keyboard로 부터 들어오는 각 Character들을 Line Buffer에 순서대로 저장
- End-of-Line Character가 들어오면 전체 Line Buffer를 OS에게 전달
- Keyboard Driver의 역할 요약
[2] Block Devices : Data transfer가 Block단위로 이뤄짐
-
Disk drive
- 하드웨어 Access가 ms 단위로 오래 걸리는 이유 :
- Seek time (Disk Arm을 목표 Track까지 이동하는데 걸리는 시간)이 길어서
- 하드웨어 Access가 ms 단위로 오래 걸리는 이유 :
-
Flash drive
-
NAND Flash Memory는 RAM과 Access Pattern이 다르다
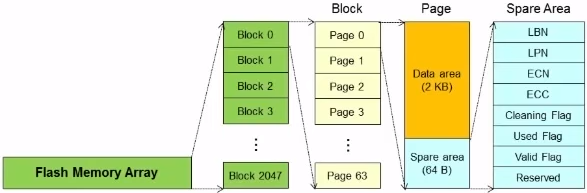
- 요기서 Page는 Memory Management에서 Page와 다름
-
Flash의 Operation :
- Read Operation (한 Page를 통채로 읽어옴) : 수행시간이 빠름
- Program(Write) Operation
- Erase Operation : Flash는 ROM이기 때문에 Rewrite이 안된다. 그래서 Write을 하기 위해서는 먼저 data를 erase한 후에 write를 해야됨. 수행시간이 제일 느림
-
Read/Write operation의 단위는 Page이고 Erase의 단위는 Block이다
-
Worn-out : Erase 가능한 횟수에 제한이 존재함
-
Wear-leveling : NAND Flash의 한 영역에 Erase가 집중되어 Worn-out이 발생하는 것을 막기 위해 전체 영역을 고루 사용하도록 조절하는 기술
-
Log structure
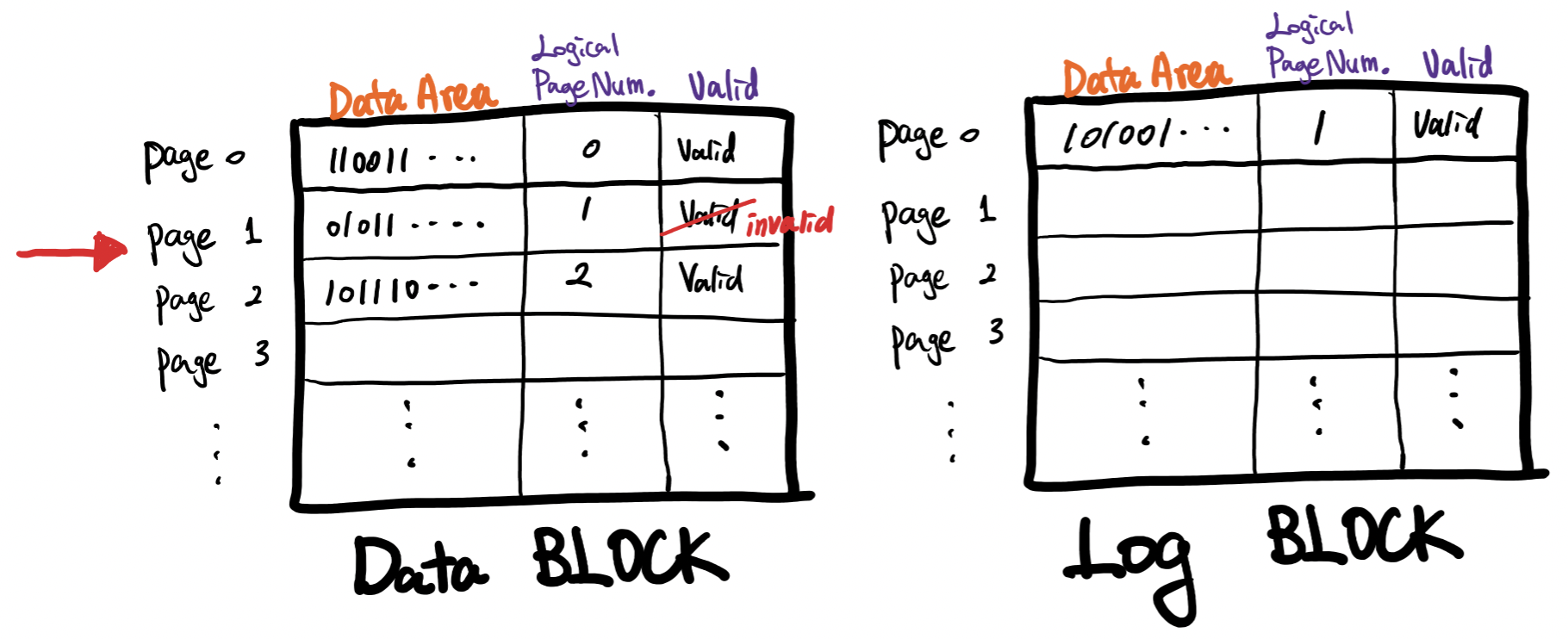
- Page 1의 내용을 update하고 싶은데 Block단위의 Erase를 하면 Data Block의 다른 Page 내용도 같이 없어지기 때문에 Log Block에다 update내용을 적고 Logical Page Number로 1을 부여한다. 그리고 Data block에 있는 옛날 Page는 invalidate한다
- 반드시 Remapping해주는 작업이 필요함
-
[3] Network Devices
- NIC (Network interface card)
Device Driver
-
Device Driver : 다른 프로그램들이 어떤 Hardware device를 잘 사용할 수 있게 해주는 Computer program
- OS와 Device사이에 위치하는 Software
- 복잡한 Device들의 특성들을 다 소화해서 User들에게 추상화된 Operation interface를 제공해줌
- UNIX계열의 Device Driver에서의 Operation들
- Open : Device를 초기화(OS관점에서 그 Device를 Register와 Device Driver가 필요한 data structure를 잡아주는 일)하는 기능
- Close : 그 Device Driver가 차지하던 공간들을 다 release 하는 기능
- Read : Input
- Write : Output
- ioctl : I/O control
- UNIX계열의 Device Driver에서의 Operation들
- UNIX에서 바라보는 Device Type
- Character Device : 주로 sequencial access
- console, keyboard, mouse, … (/dev/tty1, /dev/lp1, …)
- Block Device : 주로 random access
- hard disk drive, CD-ROM drive, … (/dev/hda1, …)
- Block Buffer Cache를 가지고 있음 (CPU에 비해 상대적으로 속도가 느린 Block Device의 성능을 보완해준다)
- Network Interfaces
- Character Device : 주로 sequencial access
-
UNIX OS에서 File system이 제공하는 역할
[1] Disk에 있는 data를 읽거나 쓸 수 있는 기능을 제공
[2] File이나 Device와 같은 System 자원들에게 Name Space를 제공
-
Device File : UNIX OS에서 특수한 file을 생성해서 file과 device를 연결시켜 놓은 것
-
directory :
/dev -
동일한 device에게 서로 다른 device driver를 제공할 수 있다
-
Device File의 내용물(content) :
-
Real Data : 말 그대로 Character content
-
Meta Data : File의 특성을 표현하는 부가적인 Data
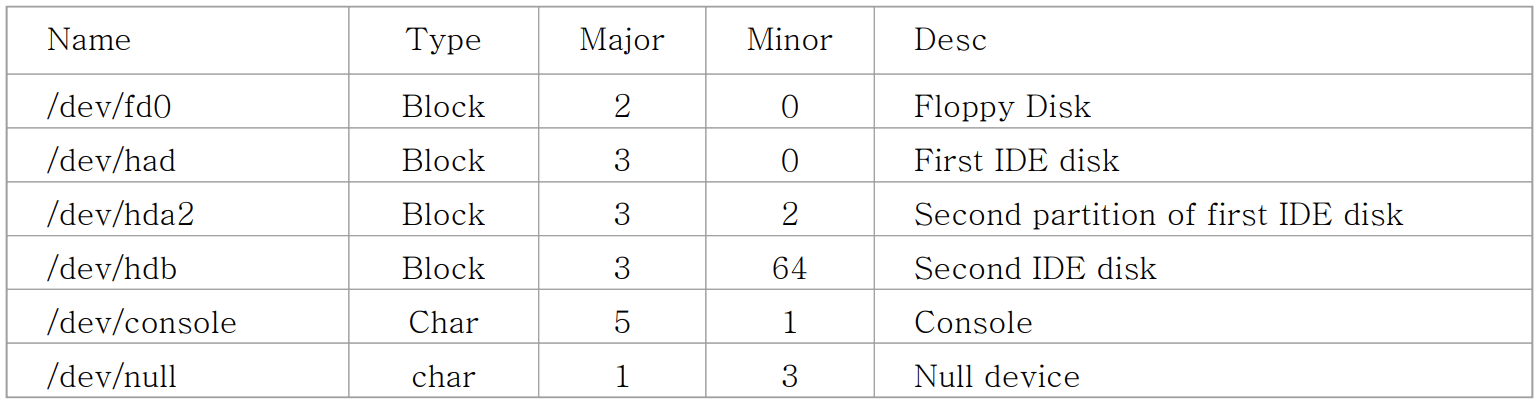
-
Major : 어떤 Type의 Device인가를 나타냄
-
Minor : device driver에 여러 routine을 호출할 때 너의 대상이 되는 device를 찾으라고 aurgment로 전달 해줌
🧐 Interesting fact :
-
The United States’ nuclear arsenal will no longer rely on a computer system that uses eight-inch floppy disks [2019/10/24]
- Pentagon was one of the several government agencies whose computer systems relied on “outdated software languages and hardware parts that are unsupported,” some of which were “at least 50 years old.”
- Upside of relying on such old technology : the systems are not connected to the internet, they are exceptionally secure (Hackers can’t break into a floppy disk)
-
-
-
-
-
Character Device Drivers
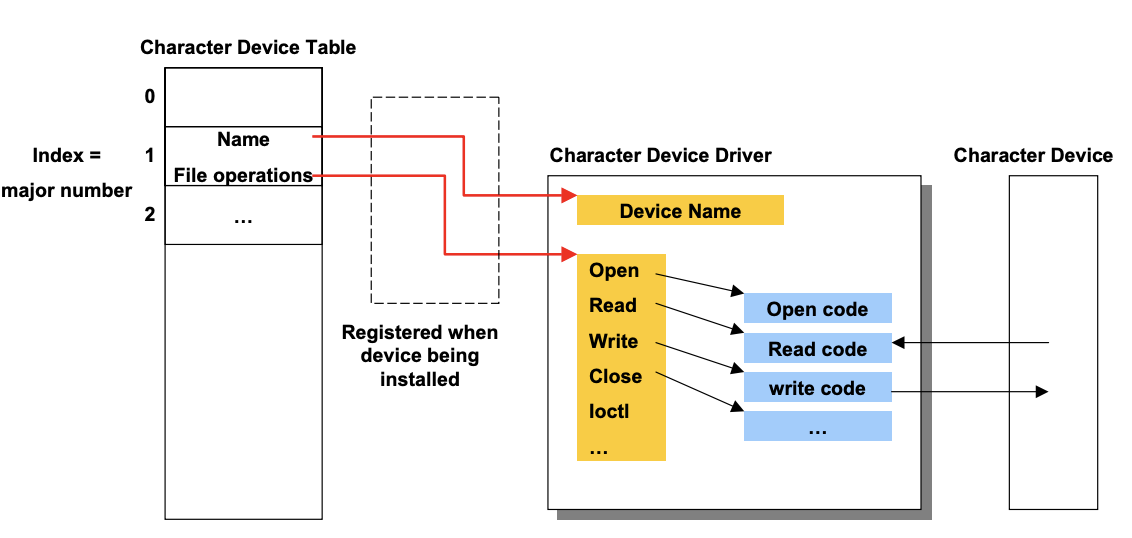
open("/dev/...")을 하게 되면 OS이 Device file을 읽어서 해당 Device table에서 File의 major number와 일치하는 entry를 찾아서 open function pointer를 얻어서 실제로 호출함- File system 입장에서 Data file이 open 됬으면 그 목적은 Disk drive에서 block을 read/write하는 건데 Device file을 open한다는 것은 Open,Close,Read,Write,ioctl 등의 함수들을 호출하는 것
-
Block Device Drivers
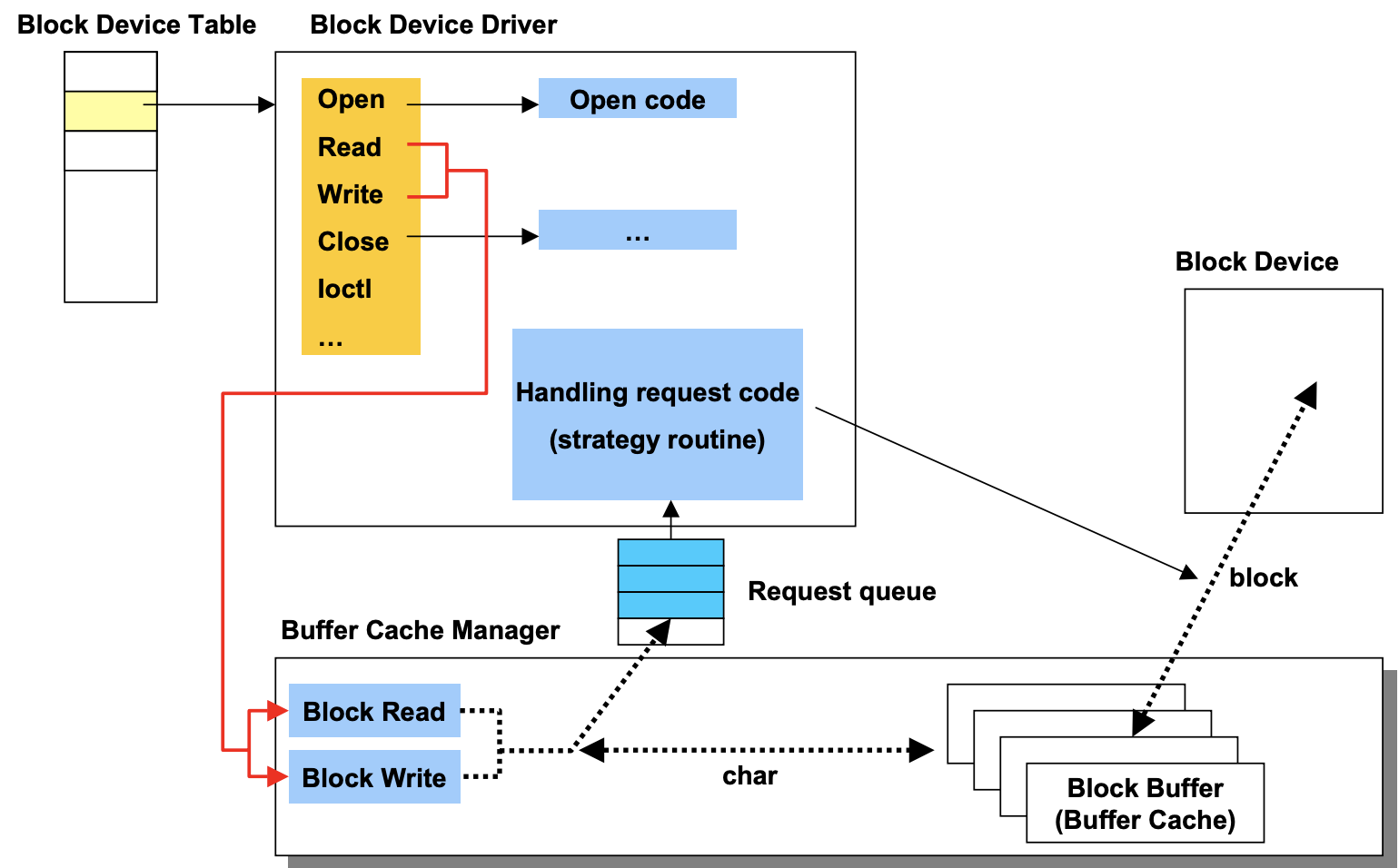
-
Device Driver가 Buffer cache를 manage하는 법
- 사용자가
read()system call을 했다면 Block read 명령으로 내부적으로 변환이 됨 - Block read 명령는 우선 Buffer cache를 접근을 함
3-a. 만약 Buffer cache내에 원하는 Block이 존재하면 거기서 바로 가져옴
3-b. 만약 Buffer cache내에 원하는 Block이 존재하지 않으면
3-b[1]. Block I/O request가 형성
3-b[2]. 관련 Device에 소속된 Request Queue로 명령이 들어감
3-b[3]. Device Driver가 제공하는 Scheduler에 의해서 Queue에 있는 Request들이 dequeue되어 실행
- 사용자가
-
-
Interrupt Handling in Device Drivers Drivers
-
Two-level processing : Linux에서 Device Interrupt 처리
-
Interrupt Service Routine이 호출되는 동안, 동일한 여러 Interrupt가 도착할 경우 Synchronization 문제가 발생하기 때문에 Handler는 최소한 자기와 동등한 수준의 Interrupt들을 Disable 시킴
-
먼저 Interrupt가 발생하면 Handler가 뜨게된다. 그럼 자기가 수행해야되는 최소한만 수행하고 나머지 중요한 Logic은 Kernel Thread 형태로 또는 User process 형태로 따로 돈다
-
Interrupt Handler의 역할 :
- 먼저 Interrupt를 Disable 시킴
- 여러 OS의 민감한 issue들을 먼저 처리해주고 나머지 logic은 Bottom half 형태로 만들어서 Bottom half Queue에 넣는다
- Bottom half는 시간이 날 때 scheduling 되며, Interrupt가 Enable된 상태에서 돌게됨
-
Bottom half
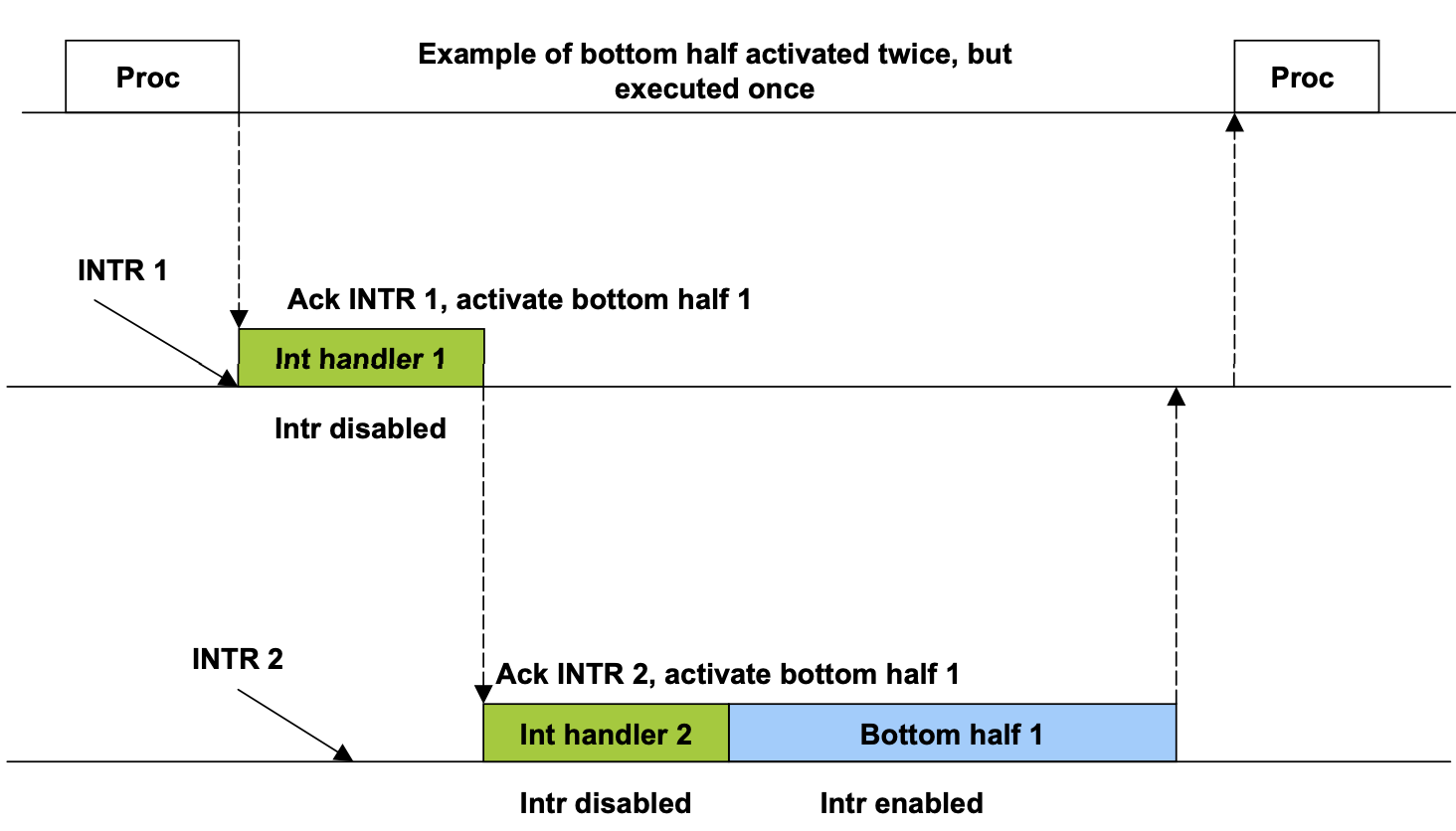
- Bottom half가 돌 때는 1개만 돈다 : 왜냐하면 한번에 떠서 여러 interrupt의 Bottom half request를 한목에 처리하기 위해서
-
-
-
Device Driver 제공하는 function들
[1] open :
- Minor number를 찾아옴
- 적절한 device를 initialize한다
- device를 사용하기 위해서 open한 process의 개수를 counter에 더함
- 나중에 close한 process는 counter에서 뺌
- counter가 0이 될 경우 전에 할당받은 data structure를 release함
- 특정 Interrupt handler를 특정 IRQ와 연동시켜서 Interrupt vector table에 등록함
[2] read/write :
-
Pooling I/O vs Interrupt Driven I/O :
- Pooling I/O : 주기적으로 Device driver가 data register에 읽어갈 값이 있는지 Check 해보는거 (정확하게는 Ready flag bit를 확인)
- Interrupt Driven I/O : 주도권을 Device를 가지고 있어서 Device가 data를 읽어오면 data register에다 쓰고 CPU한테 interrupt를 건다
-
Blocking I/O vs Non-Blocking I/O :
-
Blocking I/O : Pooling I/O의 경우 ready인지 계속 flag bit check를 반복
-
Non-Blocking I/O : Pooling I/O의 경우 ready인지 flag bit check한 다음 read가 아니면 operation을 바로 terminate
💁🏻 Embedded System, Real Time System에서는 Non-Blocking I/O를 사용
-
《Reference》