Data structure
-
Data를 저장하는 공간 + 연산들도 제공 (저장된 Data를 CRUD)
-
자료구조의 예
-
Variable
-
Array (List)
…
-
Algorithm
- 입력 데이터를 가지고 유한한 횟수의 연산들을 반복해서 정답을 출력
Data structure 와 Algorithm의 성능
Space complexity
-
프로그램을 완료하기 위해 실행해야 하는 메모리 양
-
프로그램이 실행될 때 보통 세가지 이유로 컴퓨터 메모리를 사용
- Instruction Space : 컴파일된 명령어들을 저장하는 메모리의 양
- Environmental Stack : 함수 호출시 부분적으로 실행 된 함수의 정보를 저장하는 데 사용되는 메모리의 양
- Data Space : 모든 변수와 상수를 저장하는 메모리의 양
알고리즘의 공간복잡도를 분석할 때, 보통 Data Space만을 고려
-
메모리 구조 :
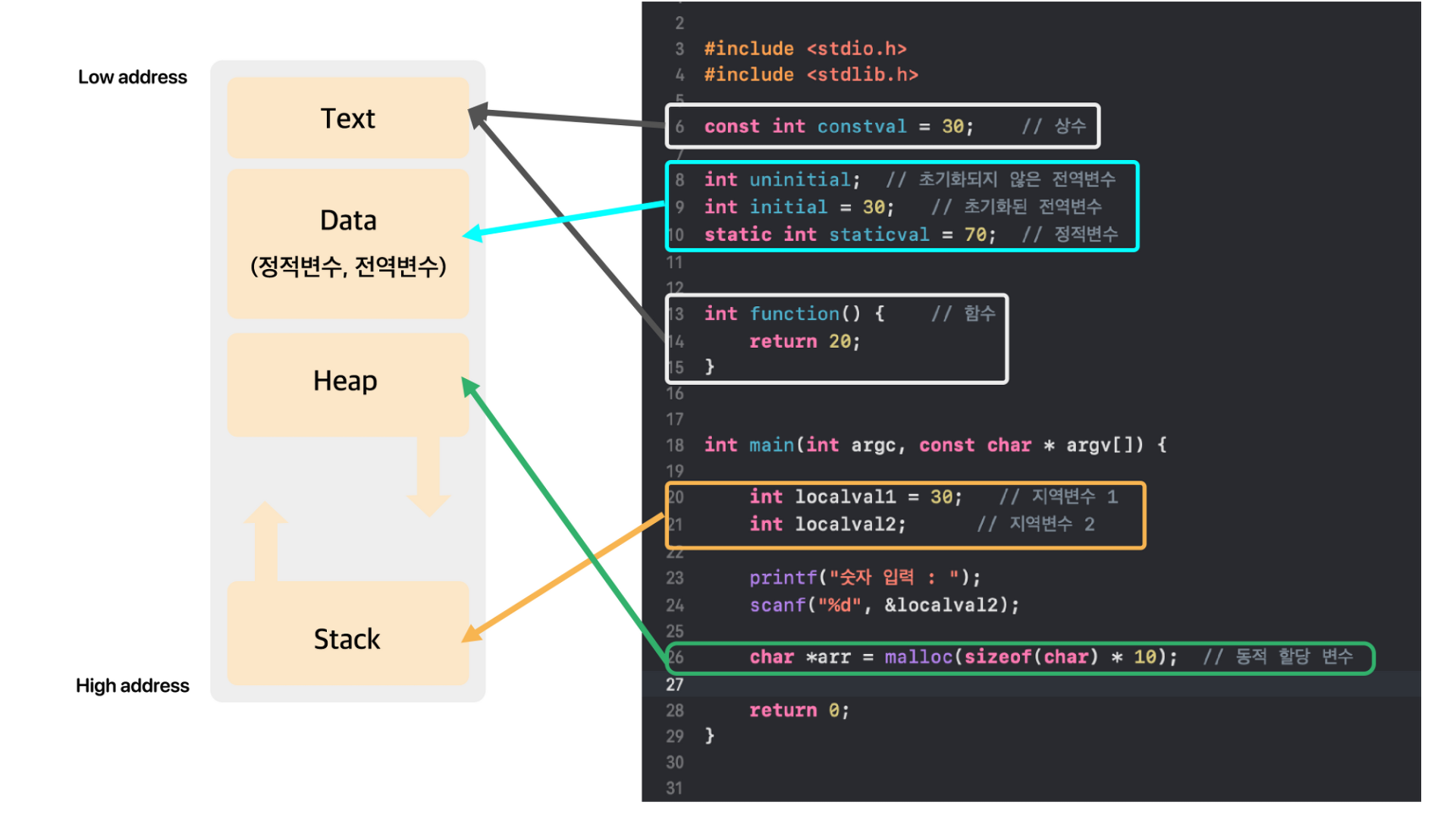
-
Text (Code) 영역
- 우리가 작성한 소스코드가 들어 가는 부분
-
Data 영역
- 전역변수와 static변수가 할당되는 영역
- 프로그램의 시작과 동시에 할당되고, 프로그램이 종료되어야 메모리가 소멸되는 영역
-
Heap 영역
- 프로그래머가 할당/해제하는 메모리 공간
- Java에서는 가비지 컬렉터가 자동으로 해제
-
Stack 영역
-
함수 호출 시 생성되는 지역 변수와 매개변수가 저장되는 영역이고, 함수 호출이 완료되면 사라짐
-
프로그램이 자동으로 사용하는 임시 메모리 영역
 Heap과 Stack영역은 사실 같은 공간을 공유
Heap과 Stack영역은 사실 같은 공간을 공유- Heap이 메모리 위쪽 주소부터 할당되면 Stack은 아래쪽부터 할당됨
- 각 영역이 상대 공간을 침범하는 일이 발생할 수 있는데 이를 각각 HEAP OVERFLOW, STACK OVERFLOW이라함
-
-
Example. Sequential Search
- 리스트에서 찾고자 하는 값을 맨 앞에서부터 끝까지 차례대로 찾아 나가는 것
public static int SequentialSearch(int[] a, int x){
int i;
for(i=0; i<a.length && a[i]!=x; i++);
if(i==a.length){
return -1;
}
return i;
}
-
Total data space : 12 bytes
x,i,0,a.length,a[i],-1(each of them cost 2 bytes)
Example. Recursive code to add a[0:n-1]
public static float Rsum(float[] a, int n){
if(n>0){
return Rsum(a, n-1) + a[n-1];
}
return 0;
}
-
Recursion stack space : 6 bytes
-
a,n,returnaddress (each of them cost 2 bytes)
-
-
Depth of recursion : n+1
Ex)
Rsum(a, 4)= Rsum(a, 3) + a[3]
= Rsum(a, 2) + a[2] + a[3]
= Rsum(a, 1) + a[1] + a[2] + a[3]
= Rsum(a, 0) + a[0] + a[1] + a[2] + a[3]
= 0 + a[0] + a[1] + a[2] + a[3]
Time complexity
-
기본 연산들 : 1단위시간 내에 할 수 있는 연산들
기본 연산 example 복사연산 = 산술연산 +, -, *, /, *, % …. 비교연산 >, >=, <, <=, ==, != 논리연산 AND, OR, NOT 비트연산 bit-AND, OR, NOT -
알고리즘의 수행시간 = 모든 입력에 대해 기본연산 횟수를 더한 수 평균
- But, 입력으로 들어올 수 있는 값들이 무한해서 현실적으로 계산이 매우 힘듬
-
알고리즘의 수행시간 = 가장 안좋은 입력에 대한 기본 연산 횟수를 측정 (worstcase time complexity)
- 어떤 입력에 대해서도 worstcase time complexity 보다 수행시간이 크지 않다
Example. finding max value from array
Input : A is array, n is size of array A Output : array index of max number Algorithm arrayMax(A,n): currentMax = A[0] --> 기본적으로 실행 (A) for i=1 to n-1 do if currentMax < A[i] --> 기본적으로 실행 (B) currentMax = A[i] --> 위에 if문이 true이면 실행 (C) return currentMax-
위의 알고리즘에서 가장 안좋은 경우는
(B)가 매번 true가 되서(C)도 실행되는 경우임. 이렇게 되기 위해선 A는 오름차순의 배열이여야 됨 ex. [2,5,7,9, …] -
가장 안좋은 입력에 대한 기본 연산 횟수를 계산해보면
-
T(n) =
(A)1번 + {for문 n-1번 실행 * ((B)1번 +(C)1번) }= 1 + {2n - 2} = 2n -1
-
Example. sum of array
Input : A is array, n is size of array A Output : sum of array Algorithm sum(A,n): sum = 0 --> 기본적으로 실행 (A) for i=1 to n-1 do for j=i to n-1 do sum = sum + (A[i]*A[j]) --> 기본적으로 실행 (B) return currentMax-
(B)을 실행할 때 진행되는 기본 연산 횟수 : 3번 (*,+,=) -
for j=i to n-1 do문 :i for j=i to n-1 do진행 횟수0 n번 1 n-1번 2 n-2번 … … n-1 1번 즉,
for i=1 to n-1 do문에서 볼 수 있드시 i=n-1까지 실행한다는 걸 알 수 있음으로for j=i to n-1 do문은 1+2+3+..+n = n(n+1)/2번 실행 -
가장 안좋은 입력에 대한 기본 연산 횟수를 계산해보면
- T(n) =
(A)1번 + (for문 n(n+1)/2번 실행 *(B)3번 ) =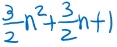
- T(n) =
-
Big-O 표기법
-
T(n)의 최고 차항만 갖고 수행시간을 표기하는 법 (최고차항 계수는 생략)
ex) T(n) =
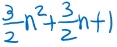 = O(n^2) , T(n) = 1 = O(1)
= O(n^2) , T(n) = 1 = O(1)
Example. Count number of bit
def number_of_bits(n): count = 0 --> 기본적으로 실행 (A) while n>0: n = n//2 --> 위에 while문이 true이면 실행 (B) count = count + 1 --> 위에 while문이 true이면 실행 (C) return count参考 :
# Python3 >>> 10 / 3 3.3333333333333335 >>> 10 // 3 3-
while n>0문 실행 횟수n=8일 경우
while문 3번 실행 (즉 count = 3)n=4일 경우
while문 2번 실행 (즉 count = 2)n=2일 경우
while문 1번 실행 (즉 count = 1)…
즉 n=n일 경우
while문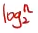 번 실행
번 실행 -
가장 안좋은 입력에 대한 기본 연산 횟수를 계산해보면
- T(n) =
(A)1번 + {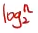 * (
* ((B)2번 +(C)2번) } = O(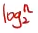 )
)
- T(n) =
-
-
Squential Data structure
Array, List
-
index로 어떤 배열의 특정 위치에 있는 값을 O(1) 시간 내에 write/read 기본 연산을 제공하는 자료구조
-
C : Array
-
읽기,쓰기 연산만 제공
-
dynamic array이 아니기 때문에 수동으로 배열의 capacity를 늘려줘야 됨
int a[4] = {2,4,0,5}; a[4] = 10; // compile error // capacity가 6인 배열을 새로 생성해서 그 배열 첫번째 주소를 b에 할당 b = (int*)malloc(6*4); // 배열 index하나에 4 byte; a = b; a[4] = 10; // 可以
-
-
Python : List
- append, pop, insert, remove, index, count 같이 다양한 연산 제공
- dynamic array : 배열의 capacity 자동조절 가능
-
시간 복잡도에 대해서 : Blog
Stack, Queue, Dequeue
-
제한된 접근 (insert, delete)만 허용
-
Stack : LIFO (Last In First Out)
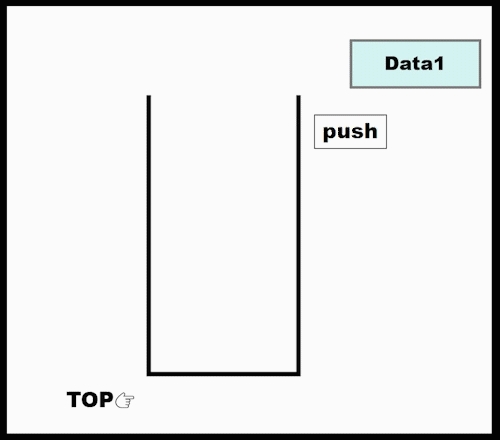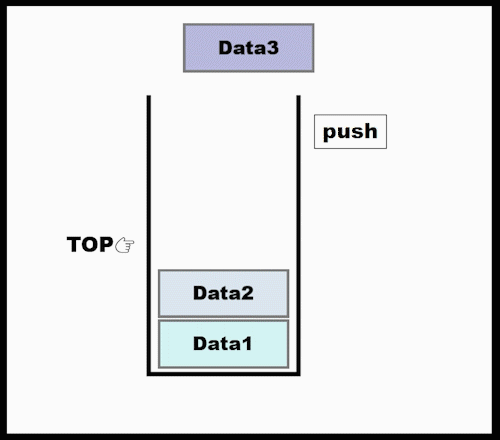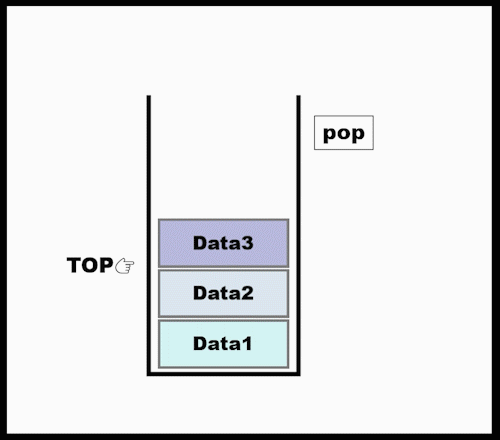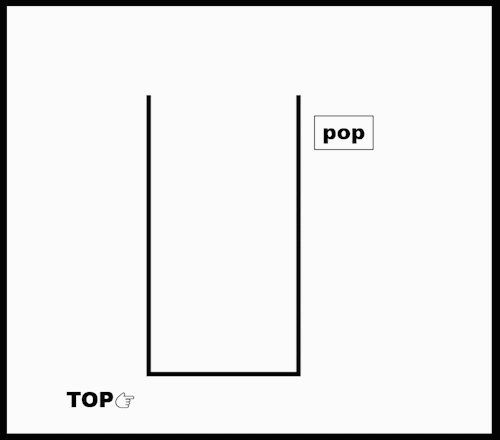
class Stack: def __init__(self): self.items = [] def push(self, val): self.item.append(val) def pop(self): try: return self.items.pop() except IndexError: print("Stack is empty") def top(): try: return self.items[-1] except IndexError: print("Stack is empty") def __len__(self): # len()로 호출하면 Stack의 item수 return return len(self.items) if __name__=="__main__": s = Stack() s.push(10) s.push(2) print(len(S))- 参考 : 클래스 내에
__init__생성자 함수는 객체가 생성될 때 자동으로 호출되기 때문에 객체를 초기화하거나 초깃값을 설정.self는 생성된 Class객체 자체를 뜻함
Example. 괄호 맞추기
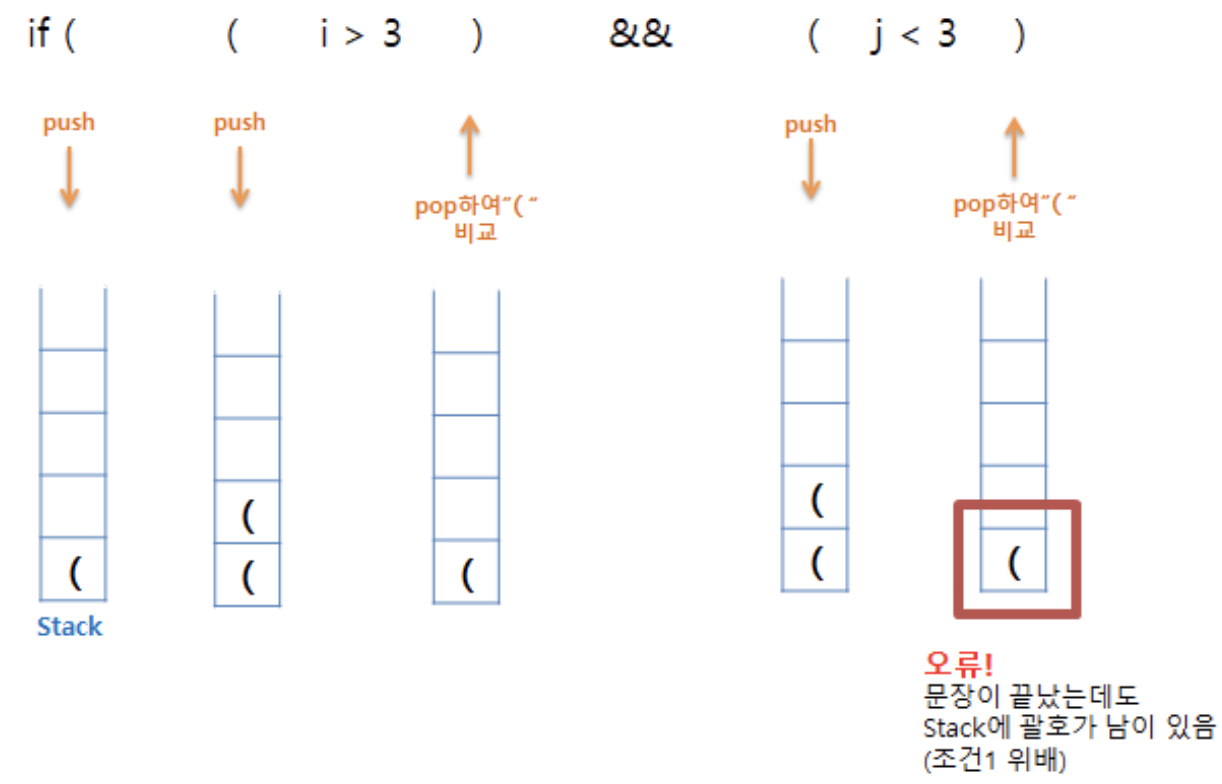
s = Stack() for character in sequence: if character == '(': s.push(character) elif character == ')': s.pop() if len(s)>0: return False else: return TrueExample. Stack을 활용한 +, -, *, / 식 계산
1) Convert Infix to post/prefix
- Infix to post/prefix 수기로 하는 법
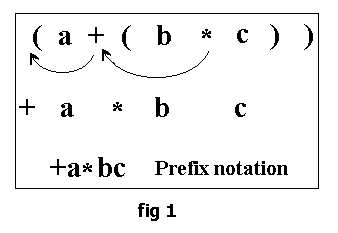
- Infix to postfix pseudocode
- outstack : postfix 결과 리턴용
- opstack : 연산자를 위한 stack
for each token in InfixExpression: if token in 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ': outstack.append(token) if token == '(': opstack.push(token) if token == ')': while opstack.top != '(': outstack.append(opstack.pop()) if opstack.top == '(': opstack.pop() if token in '+-*/': if len(opstack) != 0: while opstack.top.priority > token.priority: outstack.append(opstack.pop()) opstack.push(token) while len(opstack) != 0: outstack.append(opstack.pop())- How it works? : Youtube
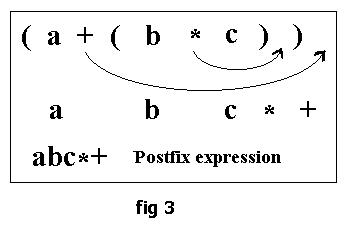
- Calculate postfix expression
- oprandStack : 피연산자 저장 Stack
for each token in PostfixExpression: if token in 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ': oprandStack.push(token) if token in '+-*/': a = oprandStack.pop() b = oprandStack.pop() oprandStack.push(calculate(a,b,token)) - 参考 : 클래스 내에
-
Queue : FIFO (First In First Out)
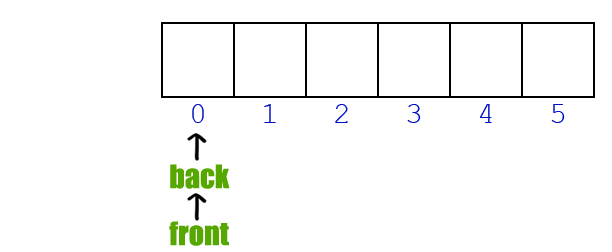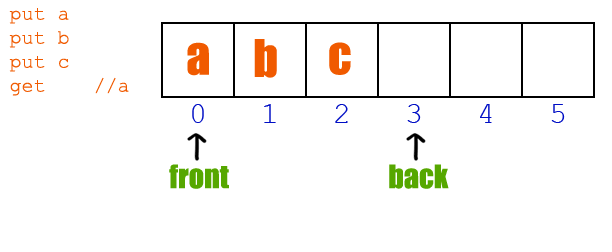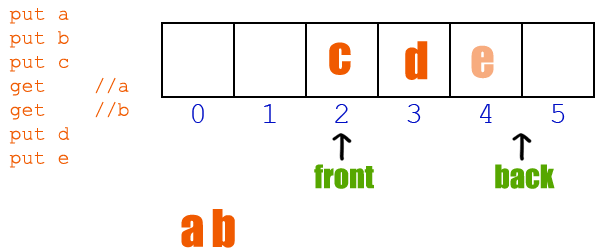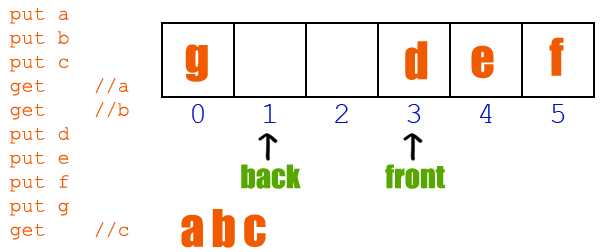
- Enqueue : Queue에서 insert
- Dequeue : Queue에서 delete
- 다음에 Dequeue될 index(
front_index)를 알아야됨
- 다음에 Dequeue될 index(
class Queue: def __init__(self): self.items = [] self.front_index = 0 def enqueue(self, val): self.item.append(val) # 요기서는 dequeue하면 원래 delete 되야되는 값을 유지한채 front_index만 이동하는 방식 def dequeue(self): if self.front_index == len(self.items): print("Queue is empty") return null else: x = self.items[front_index] self.front_index += 1 return x def __len__(self): return len(self.items)Example. Josephus Problem
-
n명의 군인들이 원형으로 있고 매 k번째 사람이 죽는걸로 하면서 최종에 살아남는 군인의 번호를 알아맞추기
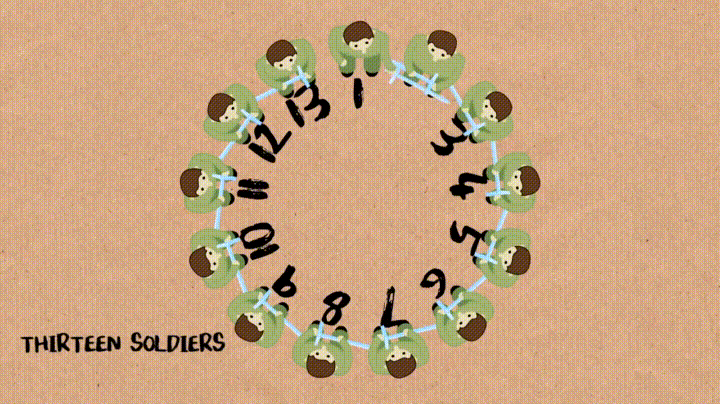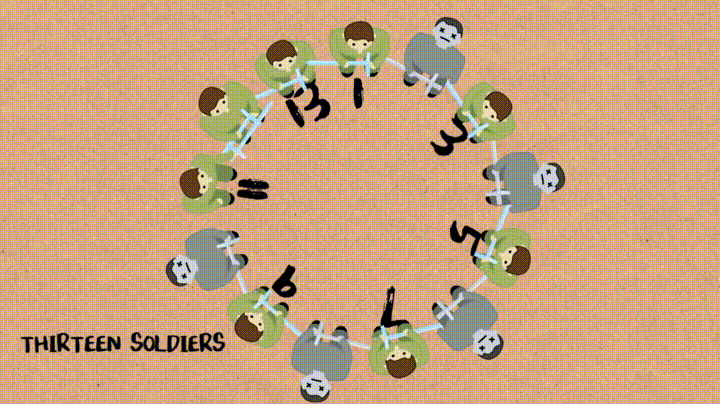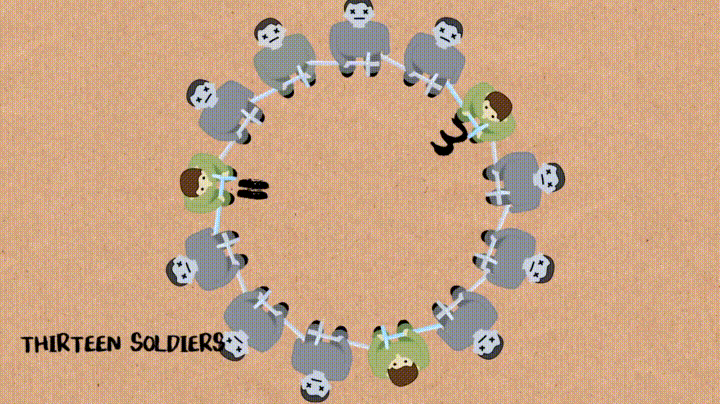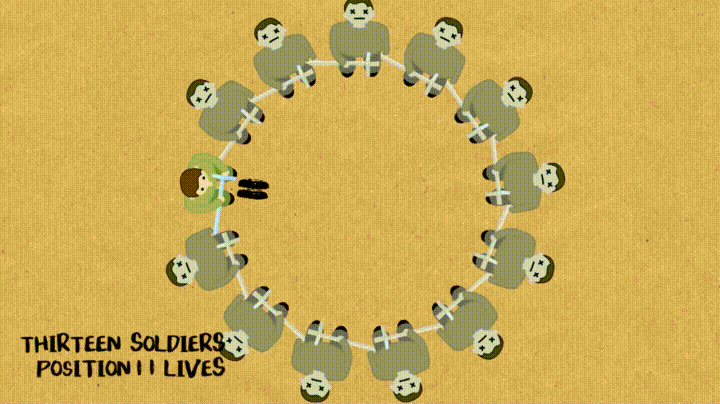
- soldierQueue : n명의 군인이 1행으로 있는 Queue
- dequeue() : dequeue되는 값을 list에서 삭제하고 삭제된 값을 return함
def josephus(soldierQueue, k): if (len(soldierQueue) == 1): return 1 else: while len(soldierQueue) != 1: for i=1 to k-1 do: soldierQueue.enqueue(soldierQueue.dequeue()) soldierQueue.dequeue() return soldierQueue.items-
밑에 과정을
soldierQueue에 값이 하나만 남을 때 까지 진행 :-
처음
k-1까지는dequeue()해서 다시enqueue()해주고k번째는dequeue()만 해줌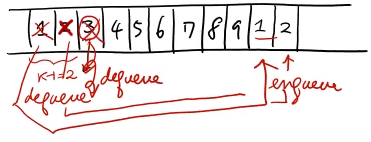
-
-
Priority Queue : 순서가 있는 상태에서 Queue를 관리
-
linked list를 활용하여 Priority Queue를 만들기
-
2가지 방법들
-
Lazy approach :
Enqueue 할 때는 그냥 element를 insert
Dequeue 할 때는 highest priority를 찾아서(sorting) 그 element를 delete
-
Early bird approach :
Enqueue 할 때는 priority에 알맞은 위치에다 element를 insert
Dequeue 할 때는 list 가장 앞에 있는 element 바로 제거
-
-
-
비교해야될 데이터가 많아질 때 linked list를 활용한 Priority Queue는 성능이 저하된다
- 그래서 binary heap을 이용해서 구하는게 일반적이다
-
binary heap : complete tree 형태면서 max heap의 성질을 가진인 binary tree
-
-
Dequeue : Stack + Queue
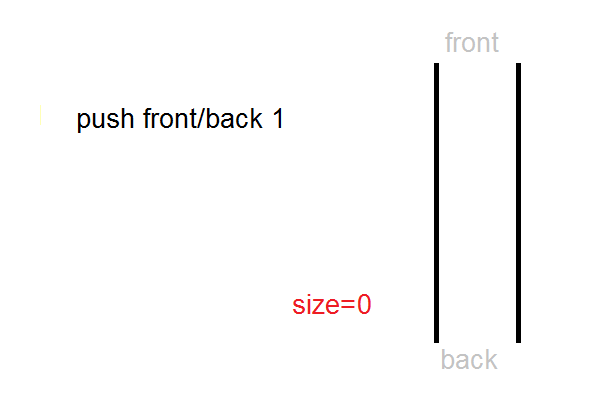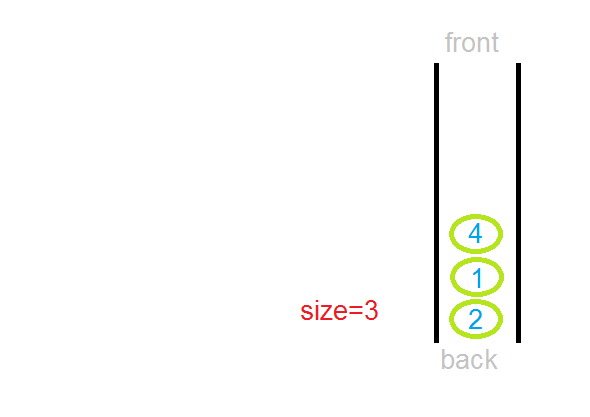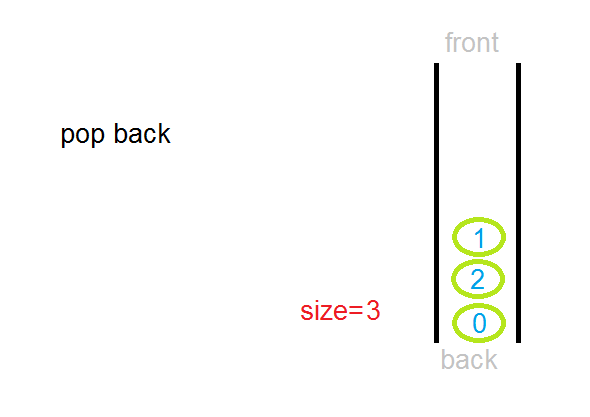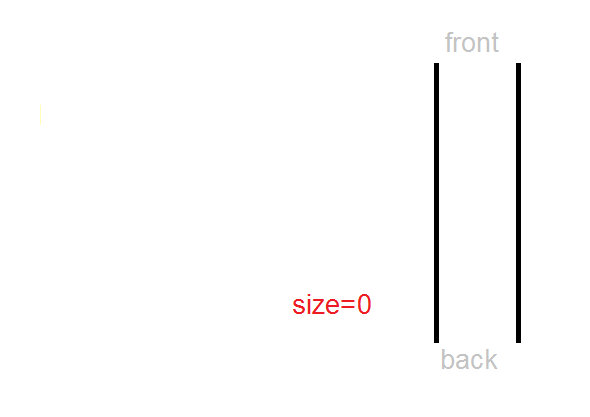
-
Delete와 Insert가 양쪽 끝에서 다 가능함
-
Python에서는 deque를 제공함
-
Linked List
- 왜 Linked List를 사용하나?
- 배열은 비슷한 유형의 선형 데이터를 저장하는데 사용할 수 있지만 제한 사항이 있음
- 배열의 크기가 고정되어 있어 미리 요소의 수에 대해 할당을 받아야 함
- 새로운 요소를 삽입하는 것은 비용이 많이 듬 (공간을 만들고, 기존 요소 전부 이동)
- 배열은 비슷한 유형의 선형 데이터를 저장하는데 사용할 수 있지만 제한 사항이 있음
-
node (data + 다음 주소 node 주소) 와 link로 연결된 구조
- head node : 가장 처음에 있는 node
- tail node : 가장 마지막에 있는 node (next pointer는 null임)
-
단점 : search 할 때는 node의 위치 만큼의 시간이 든다
- 장점 : insert 할 때는 insert 할 위치의 앞뒤 index만 알고있으면 O(1) 시간이 든다
- Array의 경우 insert를 하면 insert 뒤의 모든 index들이 이동연산을 해야됨
-
시간 복잡도에 대해서 : Blog
-
Singly Linked List
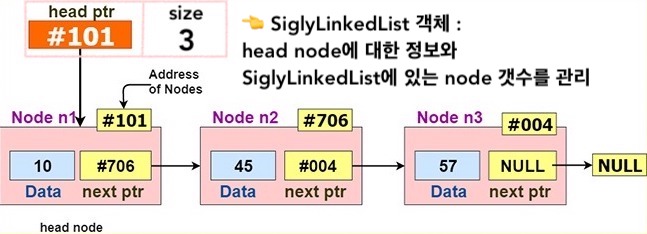
class Node: def __init__(self, data=None): self.data = data self.nextPtr = None # Node내 data를 string형으로 def __str__(self): return str(self.data) class SiglyLinkedList: def __init__(self): self.headPtr = None self.size = 0 # head node 앞에 node 추가 def pushFront(self, data): # 먼저 새로 추가하려는 node 생성 및 설정 new_node = Node(data) new_node.nextPtr = self.head # SiglyLinkedList 객체한테 head node 등록 및 size 수정 self.headPtr = new_node self.size += 1 # tail node 뒤에 node 추가 def pushBack(self, data): # 먼저 새로 추가하려는 node 생성 new_node = Node(data) if self.size == 0: # 만약 SiglyLinkedList에 아무 node가 없다면 새로운 node를 head node로 등록 self.headPtr = new_node else: # 만약 SiglyLinkedList에 node들이 존재한다면 tail node 부터 찾고 뒤에 추가 tail = self.headPtr while tail.nextPtr != None: tail = tail.nextPtr tail.nextPtr = new_node # SiglyLinkedList 객체한테 size 수정 self.size += 1 # head node 삭제 def popFront(self): if self.size == 0: # 만약 SiglyLinkedList에 아무 node가 없다면 None을 return 함 return None else: # 만약 SiglyLinkedList에 node들이 존재한다면 x = self.headPtr deleted_data = x.data # SiglyLinkedList 객체한테 (신) head node 등록 및 size 수정 self.head = x.nextPtr self.size -= 1 # (구) head node 삭제 delete(x) # 삭제된 (구) head node 데이터값 return 함 return deleted_data # tail node 삭제 def popBack(self): if self.size == 0: # 만약 SiglyLinkedList에 아무 node가 없다면 None을 return 함 return None else: # 만약 SiglyLinkedList에 node들이 존재한다면 prev, tail = None, self.headPtr # 먼저 tail node과 tail node 바로 앞에 있는 node를 찾음 while tail.nextPtr != None: prev = tail tail = tail.nextPtr if self.size == 1: # SiglyLinkedList에 node가 1개면, SiglyLinkedList 객체한테 head node 없다고 등록 self.headPtr = None else: # SiglyLinkedList에 node가 1개 이상이면 # tail node 바로 앞에 있는 node에게 tail node의 nextPtr를 넘겨줌 prev.nextPtr = tail.nextPtr deleted_data = tail.data # (구) tail node 삭제 delete(tail) self.size -= 1 # 삭제된 (구) tail node 데이터값 return 함 return deleted_data # data 값의 node를 return 함, 없다면 None을 return 함 def search(self, data): node = self.headPtr while node != None: if node.data == data: return node node = node.nextPtr return None-
pushFront과popFront는 O(1) 시간 -
pushBack과popBack는 O(n) 시간 - 즉, Singly Linked List는 head node 앞에 node를 추가하거나 head node 를 제거하는건 금방해결 할 수 있지만, tail node 뒤에 node를 추가하거나 tail node 를 제거하는건 비교적 오랜시간이 걸림
-
-
Doubly Linked List
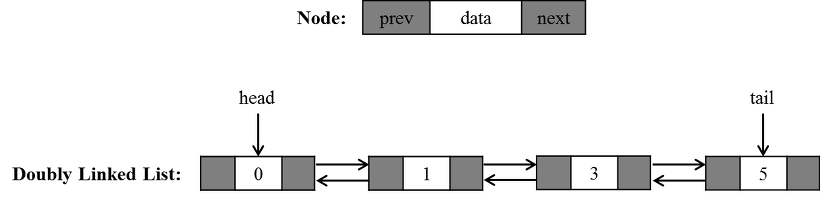
- search(data)의 시간 복잡도는 O(n)
-
Insert/delete의 시간 복잡도는 O(1) 시간
-
Circular Doubly Linked List
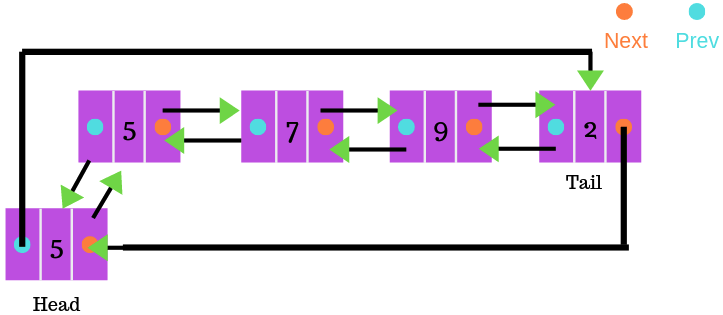
Hash Table
-
우린 divde and conquer 접근법을 통해 복잡도가 O(n^2)였던 sorting 방법을 O(n log n)으로 줄일 수 있었다
- divde and conquer 접근법을 통해 구조적으로 비교 횟수를 줄였음
-
하지만 우린 Searching 과 sorting이 비교를 안하는 방식을 적용하고 싶음
- 요즘 저장공간 많고 저렴한데 이걸 활용해서 Searching 과 sorting 시간을 줄여보자
-
slot : Hash table의 각 칸 들
-
Hash function :
- 충돌이 적도록 보장할 수 록 좋음
- hash function 자체의 computation이 빨라야됨
- But, 위에 두 조건들은 trade-off 관계가 있음
-
Collision resolution method : 충돌이 일어났을 때 해결 방법
-
Open addressing : 주위 빈칸을 찾아서 거기에 저장하는 방식
-
Linear probing
한칸씩 밑(혹은 다음)으로 가면서 빈칸을 찾는 것
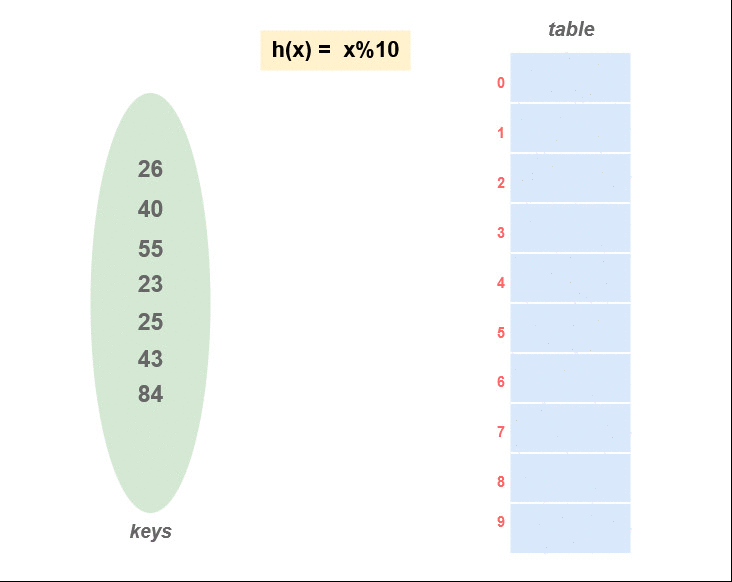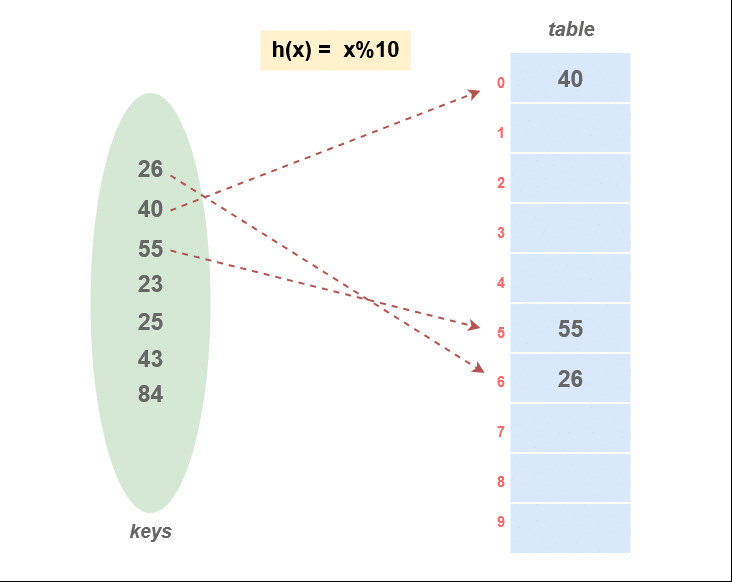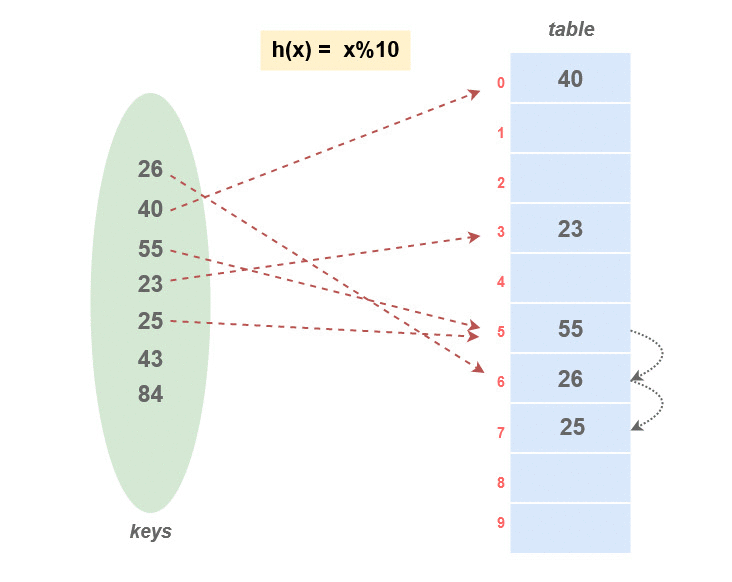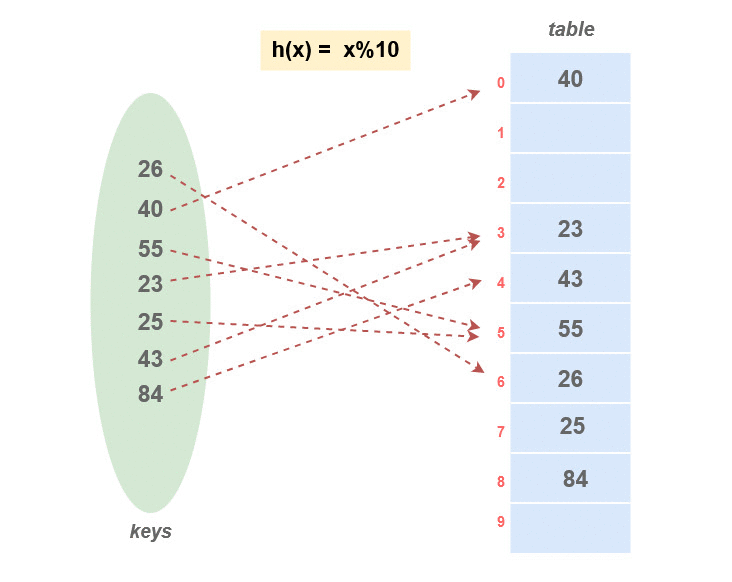
하지만 한칸씩 밑(혹은 다음)으로 가면서 빈칸이 없는 slot이 많다면 시간이 오래걸림
-
Quadratic probing
충돌 시 제곱만큼 slot을 뛰어넘어 Data 삽입
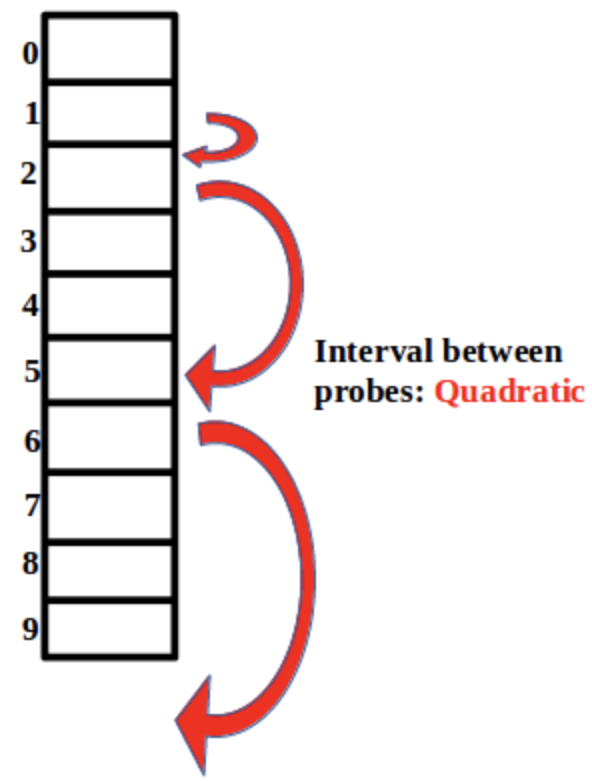
처음엔 1^2칸 넘어가서 빈칸인지 확인, 근데 그 slot이 빈칸이 아니면 2^2칸을 뛰어넘고 …
-
Double hasing
Hash 충돌 시 다른 Hash function을 한번 더 적용
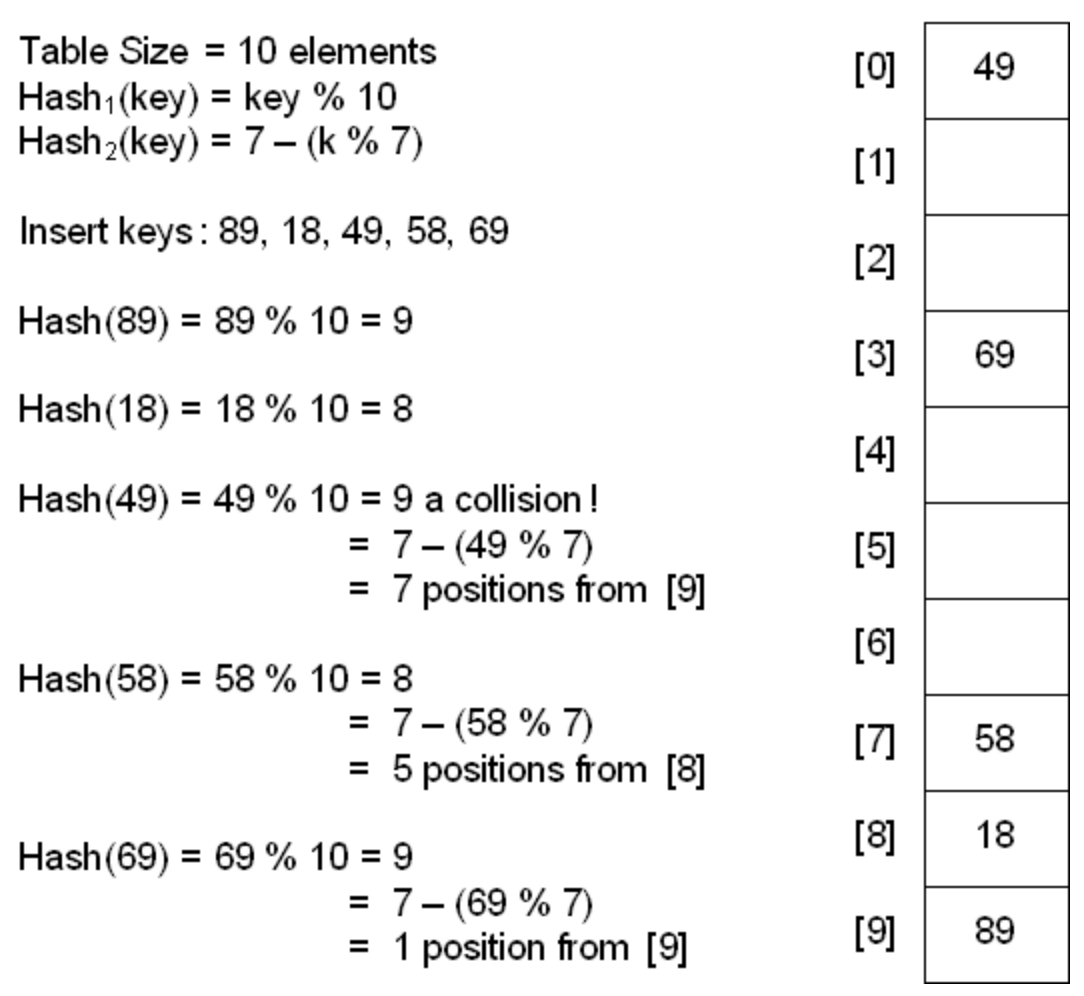
-
Open addressing의 Deletion
-
Lazy Deletion :
각 slot에 data와 해당 데이터 유무상태에 대한 bool 값이 있음. 그래서 삭제가 일어날 경우 실제로 data는 지워지지 않았으나 bool값에 지워졌다고 설정
나중에 한번 더 큰 size의 hash table로 옮길때 bool값에 지워졌다고 설정된 slot은 옮기지 않음
-
-
-
Chaining (Closed addressing)
같은 해쉬값을 갖는 데이터를 linked list에 사슬 모양으로 연결
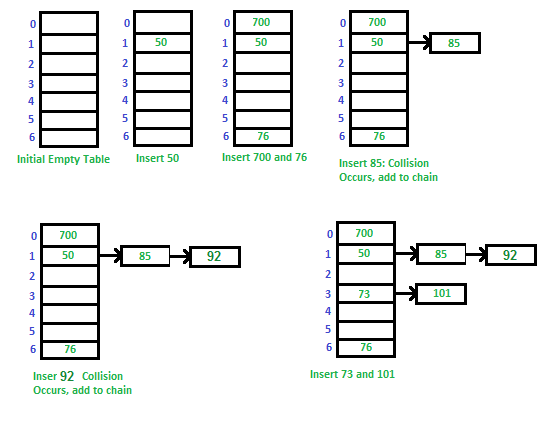
검색 시간이 O (n)이 될 수 있음
-
Open addressing
 Chaining
Chaining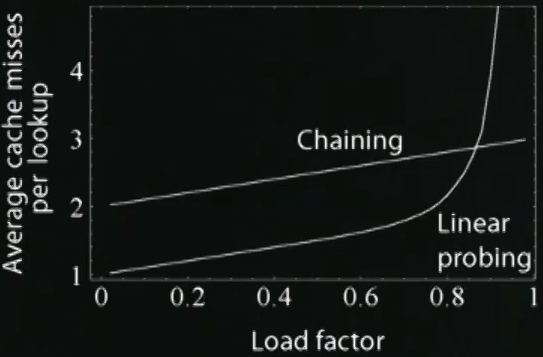
- Load factor, 즉 hash table에 입력된 값이 점점 많아지면 Chaining 보다 Open addressing의 search time이 더 커질 것 이다
-
《Reference》